We take
action,
not sides
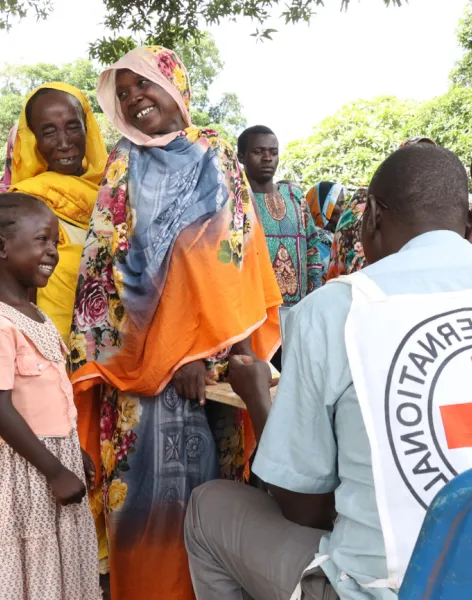
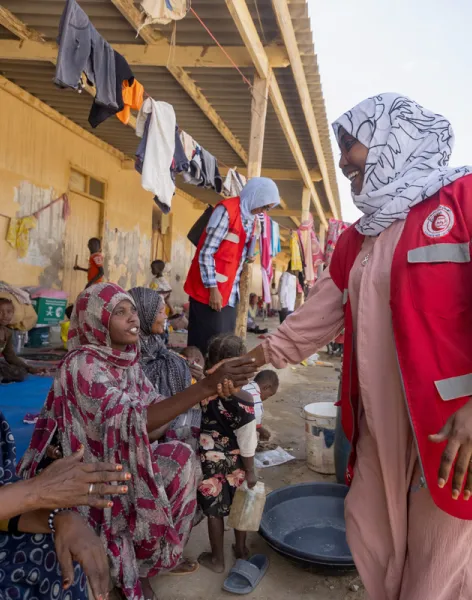
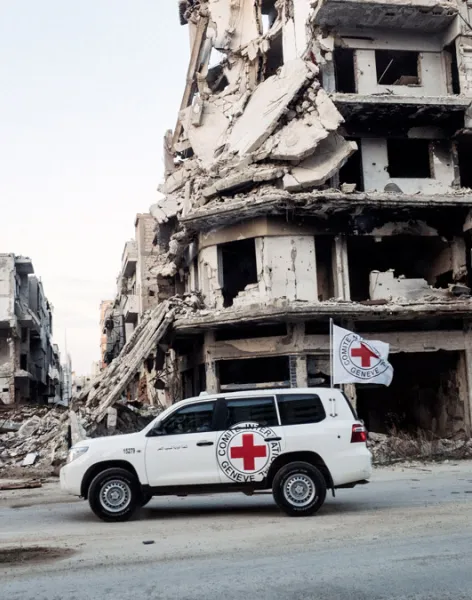
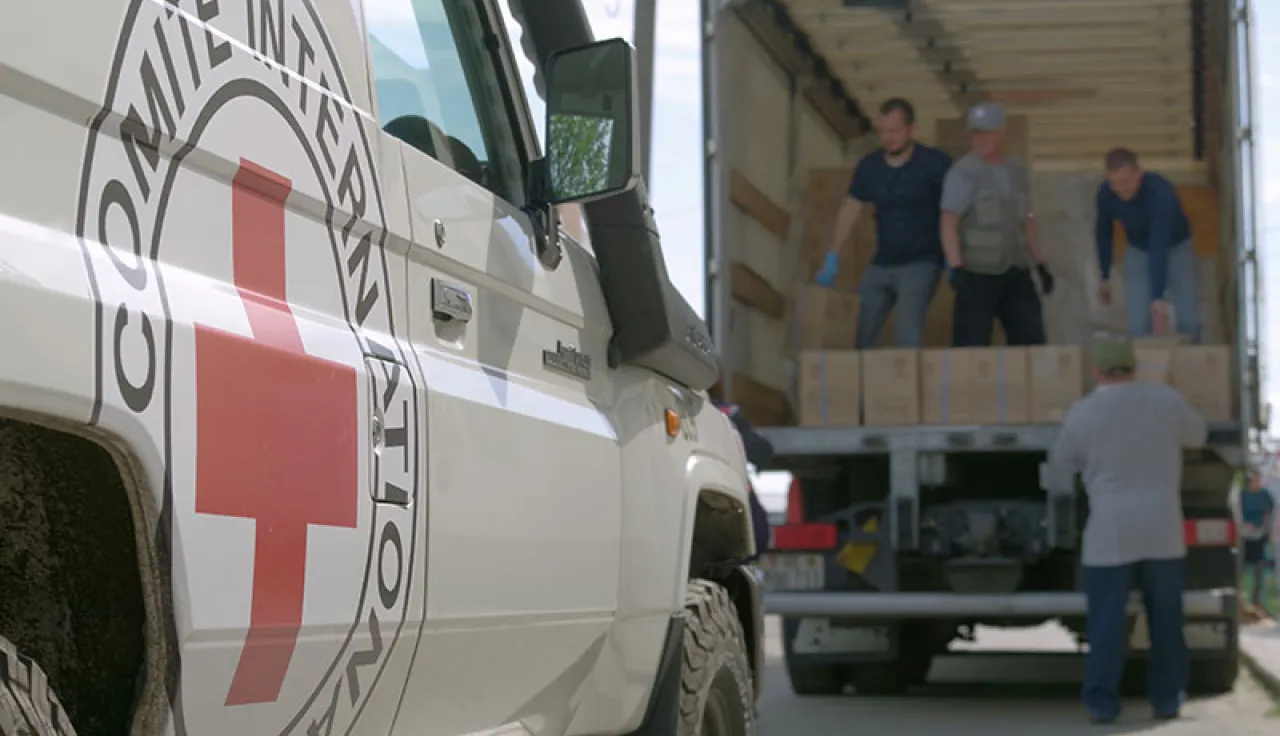
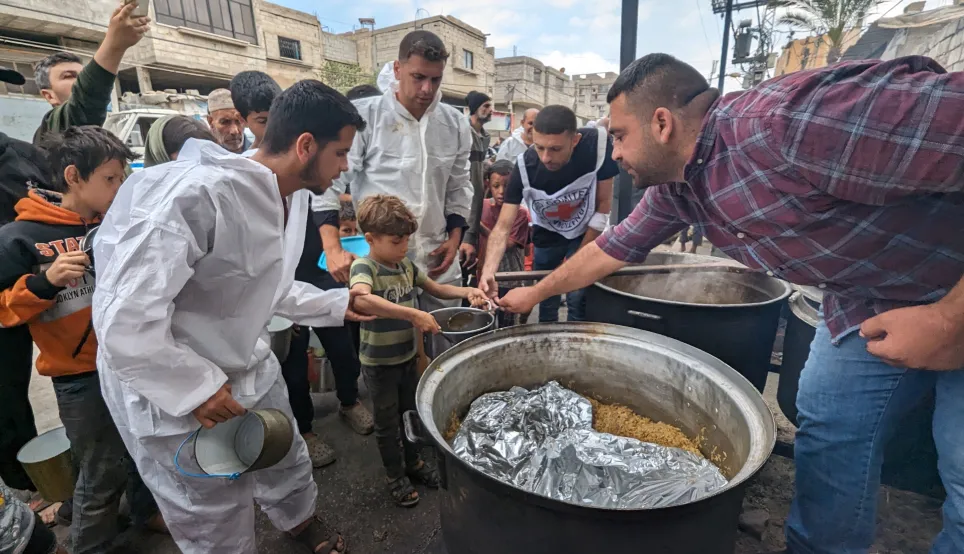
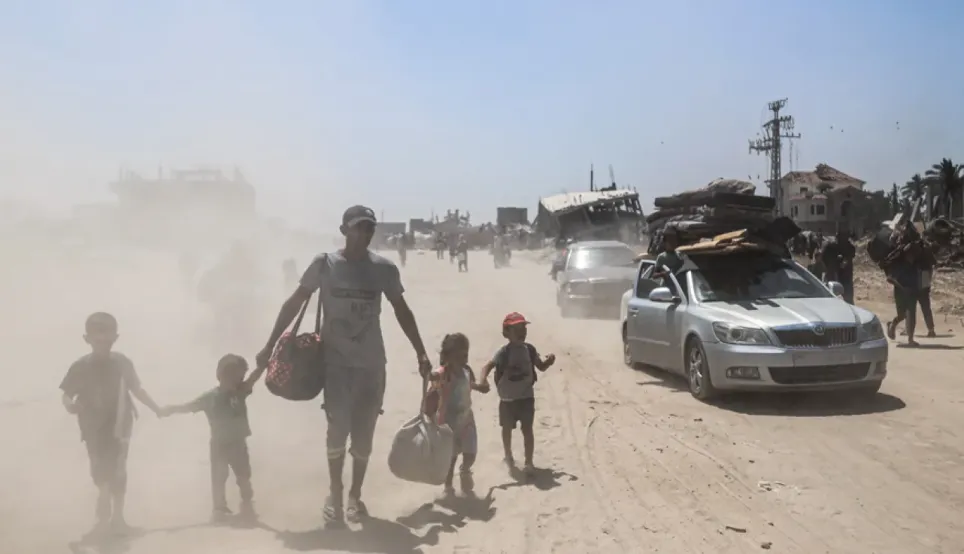
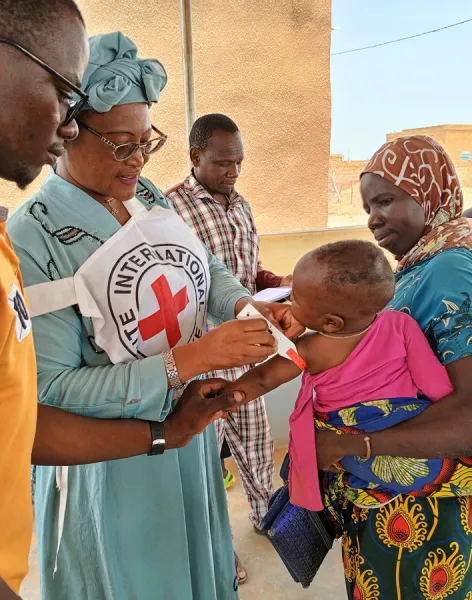
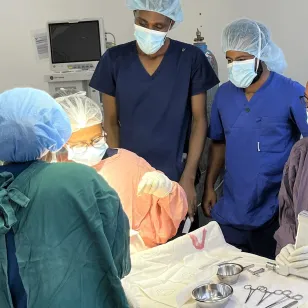
Because we are neutral, impartial and independent, we can reach those who need us when others cannot, providing humanitarian assistance, protecting lives, upholding rights, and relieving the suffering of people around the world whose lives have been torn apart by armed conflict and violence.